 |
LArSoft
v07_13_02
Liquid Argon Software toolkit - http://larsoft.org/
|
 |
LArSoft
v07_13_02
Liquid Argon Software toolkit - http://larsoft.org/
|
Namespace for general, non-LArSoft-specific utilities. More...
Namespaces | |
| details | |
| flags | |
| Classes and functions to manage bit masks and flags. | |
| manip | |
Classes | |
| struct | add_tag |
| struct | always_false_type |
A std::false_type with a template argument. More... | |
| struct | always_true_type |
A std::true_type with a template argument. More... | |
| struct | collection_value_access_type |
Trait of type obtained by access to element of collection Coll. More... | |
| struct | collection_value_constant_access_type |
Trait of type obtained by constant access to element of collection Coll. More... | |
| struct | collection_value_type |
Trait of value contained in the template collection Coll. More... | |
| struct | count_extracted_types |
Counts the elements of a tuple-like type containing a Target type. More... | |
| struct | count_type_in_tuple |
Holds whether the Target type is element of the specified std::tuple. More... | |
| struct | count_type_in_tuple< Target, std::tuple< T... > > |
| class | DatabaseUtil |
| class | DataProductChangeTracker_t |
| Detects the presence of a new event or data product. More... | |
| class | DetectorPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT |
| class | EventChangeTracker_t |
| Detects the presence of a new event. More... | |
| struct | extract_to_tuple_type |
Returns type TargetClass<U...> from a SrcTuple<T...>. More... | |
| class | FileCatalogMetadataExtras |
| class | GaussianEliminationAlg |
| class | GeometryUtilities |
| class | GridContainerBase1D |
| Base class for a container of data arranged on a 1D-grid. More... | |
| class | GridContainerBase2D |
| Base class for a container of data arranged on a 2D-grid. More... | |
| class | GridContainerBase3D |
| Base class for a container of data arranged on a 3D-grid. More... | |
| class | GridContainerIndicesBase1D |
| Index manager for a container of data arranged on a >=1-dim grid. More... | |
| class | GridContainerIndicesBase2D |
| Index manager for a container of data arranged on a >=2-dim grid. More... | |
| class | GridContainerIndicesBase3D |
| Index manager for a container of data arranged on a >=3-dim grid. More... | |
| struct | has_duplicate_extracted_types |
Traits holding whether elements of Tuple have duplicate types. More... | |
| struct | has_extracted_type |
Trait holding whether an element in Tuple type contains Target. More... | |
| struct | index_of_extracted_type |
Returns the index of the element in Tuple with the specified type. More... | |
| struct | KeepByPositionFilterTag |
| Tag for filters. More... | |
| class | LArFFT |
| class | LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT |
| Properties related to liquid argon environment in the detector. More... | |
| class | LazyVector |
| A contiguous data container expanded on write. More... | |
| class | NormalDistribution |
| class | PlaneDataChangeTracker_t |
| Detects the presence of a new event, data product or wire plane. More... | |
| class | PositionInVolumeFilter |
| Use to keep particles with at least part of trajectory in a volume. More... | |
| class | PxHit |
| class | PxHitConverter |
| class | PxLine |
| class | PxPoint |
| class | Range |
| represents a "Range" w/ notion of ordering. A range is defined by a pair of "start" and "end" values. This is stored in std::pair attribute util::Range::_window. This attribute is protected so that the start/end cannot be changed w/o a check that start is always less than end. Note the specialization requires a template class T to have less operator implemented. More... | |
| struct | RangeForWrapperTag |
| Tag marking the use of RangeForWrapperBox. More... | |
| struct | remove_tag |
Trait holding the type contained in a TaggedType (or the type itself). More... | |
| struct | remove_tag< TaggedType< T, Tag > > |
| class | RootGraphicsEnablingService |
| Trojan service to inject initialization code. More... | |
| struct | self_type |
| Trait returning the very same type as in the template argument. More... | |
| class | SignalShaping |
| class | SumSecondFunction |
| struct | TagExtractor |
| Extracts the tag from a type. More... | |
| struct | TaggedType |
| A type with a specified tag. More... | |
| struct | TagN |
| Tag class parametrized by a sequence of numbers. More... | |
| class | TensorIndices |
| Converts a tensor element specification into a linear index. More... | |
| class | TensorIndices< 1U > |
| struct | TensorIndicesBasicTypes |
| Types for TensorIndices class. More... | |
| class | UBDaqID |
| class | UniqueRangeSet |
| std::set of util::Range, which does not allow any overlap in contained element. std::set<Range> w/ modified insert/emplace function. Original std::set does not allow modification of element. I assume what we're interested in is "find if the range already \n exists, and merge if it exists". The insert function does that by recursively looking up overlapping elements w.r.t. input argument of insert function. More... | |
| class | UtilException |
| class | VectorMap |
Typedefs | |
| template<typename Coll > | |
| using | collection_value_t = typename collection_value_type< Coll >::type |
Type contained in the collection Coll. More... | |
| template<typename Coll > | |
| using | collection_value_access_t = typename collection_value_access_type< Coll >::type |
Type obtained by constant access to element of collection Coll. More... | |
| template<typename Coll > | |
| using | collection_value_constant_access_t = typename collection_value_constant_access_type< Coll >::type |
Type obtained by constant access to element of collection Coll. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| using | self_t = typename self_type< T >::type |
| The very same type as in the template argument. More... | |
| template<bool Value> | |
| using | bool_constant = std::integral_constant< bool, Value > |
| template<typename BoolTrait > | |
| using | negation = bool_constant<!BoolTrait::value > |
| template<typename A , typename B > | |
| using | is_not_same = negation< std::is_same< A, B >> |
| typedef int | UBLArSoftCh_t |
| typedef std::map< UBDaqID, UBLArSoftCh_t > | UBChannelMap_t |
| typedef std::map< UBLArSoftCh_t, UBDaqID > | UBChannelReverseMap_t |
| using | GridContainer2DIndices = GridContainerIndicesBase2D<> |
| Index manager for a container of data arranged on a 2D grid. More... | |
| using | GridContainer3DIndices = GridContainerIndicesBase3D<> |
| Index manager for a container of data arranged on a 3D grid. More... | |
| template<typename DATUM > | |
| using | GridContainer2D = GridContainerBase2D< DATUM, GridContainer2DIndices > |
| Container allowing 2D indexing. More... | |
| template<typename DATUM > | |
| using | GridContainer3D = GridContainerBase3D< DATUM, GridContainer3DIndices > |
| Container allowing 3D indexing. More... | |
| using | LArPropertiesArgoNeuT = LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT |
| type of provider name following LArSoft name convention More... | |
| using | MatrixIndices = TensorIndices< 2U > |
| Type for indexing a 2D-tensor (matrix) More... | |
| template<typename SrcTuple , template< typename T, typename... > class Extractor, template< typename... > class TargetClass = std::tuple> | |
| using | extract_to_tuple_type_t = typename extract_to_tuple_type< SrcTuple, Extractor, TargetClass >::type |
Direct access to the type in extract_to_tuple_type. More... | |
| template<typename Tuple , template< typename... > class TargetClass = std::tuple> | |
| using | to_tuple = extract_to_tuple_type< Tuple, self_type, TargetClass > |
| template<typename Tuple , template< typename... > class TargetClass = std::tuple> | |
| using | to_tuple_t = typename to_tuple< Tuple, TargetClass >::type |
Direct access to the type in to_tuple. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| using | index_of_type = index_of_extracted_type< self_type, Target, Tuple > |
| template<template< typename T, typename... > class Extractor, typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| using | type_with_extracted_type = std::tuple_element< index_of_extracted_type_v< Extractor, Target, Tuple >, Tuple > |
Returns the element type in Tuple with the specified type. More... | |
| template<template< typename T, typename... > class Extractor, typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| using | type_with_extracted_type_t = typename type_with_extracted_type< Extractor, Target, Tuple >::type |
Direct access to the value in type_with_extracted_type. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| using | has_type = has_extracted_type< self_type, Target, Tuple > |
| template<typename Tuple > | |
| using | has_duplicate_types = has_duplicate_extracted_types< self_type, Tuple > |
| template<typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| using | count_types = count_extracted_types< self_type, Target, Tuple > |
| template<typename T , typename Tag > | |
| using | add_tag_t = typename add_tag< T, Tag >::type |
| template<typename Tagged > | |
| using | remove_tag_t = typename remove_tag< Tagged >::type |
Direct access to the type contained in remove_tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tagged > | |
| using | tag_of = TagExtractor< Tagged > |
Trait holding the tag of Tagged as type. More... | |
| template<typename Tagged > | |
| using | tag_of_t = typename tag_of< Tagged >::type |
Direct access to the type in tag_of. More... | |
| template<typename SrcTuple > | |
| using | extract_tags = extract_to_tuple_type< SrcTuple, TagExtractor > |
Returns a tuple with all the tags from SrcTuple. More... | |
| template<typename SrcTuple > | |
| using | extract_tags_t = typename extract_tags< SrcTuple >::type |
Direct access to the type in extract_tags. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| using | index_of_tag = index_of_extracted_type< TagExtractor, Tag, Tuple > |
Trait holding the index of the element of Tuple with tag Tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| using | type_with_tag = type_with_extracted_type< TagExtractor, Tag, Tuple > |
Trait holding the type of the element of Tuple with tag Tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| using | type_with_tag_t = typename type_with_tag< Tag, Tuple >::type |
Direct access to the value in type_with_tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| using | has_tag = has_extracted_type< TagExtractor, Tag, Tuple > |
Trait informing if there are elements in Tuple with tag Tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| using | count_tags = count_extracted_types< TagExtractor, Tag, Tuple > |
Trait counting the elements in Tuple with tag Tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tuple > | |
| using | has_duplicate_tags = has_duplicate_extracted_types< TagExtractor, Tuple > |
Trait reporting if multiple elements in Tuple have the same tag. More... | |
Functions | |
| template<typename Coll > | |
| auto | makePointerVector (Coll &coll) |
| Creates a STL vector with pointers to data from another collection. More... | |
| template<typename Coll , typename PtrColl > | |
| void | MoveFromPointers (Coll &dest, PtrColl &src) |
| Moves the content from a collection of pointers to one of data. More... | |
| template<typename Coll , typename Sorter > | |
| void | SortByPointers (Coll &coll, Sorter sorter) |
| Applies sorting indirectly, minimizing data copy. More... | |
| template<typename T = double> | |
| constexpr T | pi () |
| Returns the constant pi (up to 35 decimal digits of precision) More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| constexpr T | DegreesToRadians (T angle) |
| Converts the argument angle from degrees into radians. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| constexpr T | RadiansToDegrees (T angle) |
Converts the argument angle from radians into degrees ( 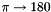 ) More... ) More... | |
| template<typename Stream , typename Left , typename Right , typename Data > | |
| void | DumpAssociationsIntro (Stream &&out, art::Assns< Left, Right, Data > const &assns) |
| Dumps a short introduction about specified association. More... | |
| template<class PRODUCER , class T , class U > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, std::vector< T > const &a, art::Ptr< U > const &b, art::Assns< U, T > &assn, std::string a_instance, size_t indx=UINT_MAX) |
| Creates a single one-to-one association. More... | |
| template<class PRODUCER , class T , class U > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, std::vector< T > const &a, art::Ptr< U > const &b, art::Assns< U, T > &assn, size_t indx=UINT_MAX) |
| Creates a single one-to-one association. More... | |
| template<class PRODUCER , class T , class U > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, art::Ptr< T > const &a, art::Ptr< U > const &b, art::Assns< U, T > &assn) |
| Creates a single one-to-one association. More... | |
| template<class PRODUCER , class T , class U > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, std::vector< T > const &a, art::PtrVector< U > const &b, art::Assns< T, U > &assn, size_t indx=UINT_MAX) |
| Creates a single one-to-many association. More... | |
| template<class PRODUCER , class T , class U > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, art::Ptr< T > const &a, std::vector< art::Ptr< U >> const &b, art::Assns< T, U > &assn) |
| Creates a single one-to-many association. More... | |
| template<class PRODUCER , class T , class U > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, std::vector< T > const &a, std::vector< art::Ptr< U >> const &b, art::Assns< T, U > &assn, size_t indx=UINT_MAX) |
| Creates a single one-to-many association. More... | |
| template<class PRODUCER , class T , class U > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, std::vector< T > const &a, std::vector< U > const &b, art::Assns< T, U > &assn, size_t startU, size_t endU, size_t indx=UINT_MAX) |
| Creates a single one-to-many association. More... | |
| template<class PRODUCER , class T , class U > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, std::vector< T > const &a, std::vector< U > const &b, art::Assns< T, U > &assn, std::vector< size_t > const &indices, size_t indx=UINT_MAX) |
| Creates a single one-to-many association. More... | |
| template<typename PRODUCER , typename T , typename U , typename Iter > | |
| bool | CreateAssn (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, art::Assns< T, U > &assn, size_t first_index, Iter from_second_index, Iter to_second_index) |
| Creates a single one-to-many association. More... | |
| template<class T , class U > | |
| std::vector< const U * > | FindUNotAssociatedToT (art::Handle< U > b, art::Event const &evt, std::string const &label) |
| template<class T , class U > | |
| std::vector< art::Ptr< U > > | FindUNotAssociatedToTP (art::Handle< U > b, art::Event const &evt, std::string const &label) |
| template<class T , class U > | |
| std::vector< size_t > | GetAssociatedVectorOneI (art::Handle< art::Assns< T, U > > h, art::Handle< std::vector< T > > index_p) |
| template<class T , class U > | |
| std::vector< const U * > | GetAssociatedVectorOneP (art::Handle< art::Assns< T, U > > h, art::Handle< std::vector< T > > index_p) |
| template<class T , class U > | |
| std::vector< std::vector< size_t > > | GetAssociatedVectorManyI (art::Handle< art::Assns< T, U > > h, art::Handle< std::vector< T > > index_p) |
| template<class T , class U > | |
| std::vector< std::vector< const U * > > | GetAssociatedVectorManyP (art::Handle< art::Assns< T, U > > h, art::Handle< std::vector< T > > index_p) |
| template<typename Range , typename Pred > | |
| auto | filterRangeFor (Range &&range, Pred &&pred) -> decltype(auto) |
| Provides iteration only through elements passing a condition. More... | |
| template<class A , class F > | |
| void | for_each_associated_group (A const &assns, F &func) |
| Helper functions to access associations in order. More... | |
| template<class A > | |
| auto | associated_groups (A const &assns) |
| Helper functions to access associations in order. More... | |
| template<class A > | |
| auto | associated_groups_with_left (A const &assns) |
| Helper functions to access associations in order, also with key. More... | |
| template<typename Groups > | |
| auto | groupByIndex (Groups &&groups, std::size_t index) -> decltype(auto) |
Returns the group within groups with the specified index. More... | |
| template<typename Coll , typename KeyOf > | |
| std::vector< size_t > | MakeIndex (Coll const &data, KeyOf key_of=KeyOf()) |
| Creates a map of indices from an existing collection. More... | |
| template<typename Coll , typename KeyOf > | |
| auto | MakeMap (Coll const &data, KeyOf key_of=KeyOf()) -> std::vector< decltype(key_of(*(data.begin()))) const * > |
| Creates a map of objects from an existing collection. More... | |
| template<typename Range > | |
| auto | wrapRangeFor (Range &&range) -> decltype(auto) |
| Wraps an object for use in a range-for loop. More... | |
| template<typename Range > | |
| auto | operator| (Range &&range, RangeForWrapperTag) -> decltype(auto) |
| Transforms a range so that it can be used in a range-for loop. More... | |
| template<unsigned int RANK1, unsigned int RANK2, typename = std::enable_if_t<(RANK1 != RANK2), bool>> | |
| bool | operator== (TensorIndices< RANK1 > const &a, TensorIndices< RANK2 > const &b) |
| Comparison operator with tensors of different rank. More... | |
| template<unsigned int RANK1, unsigned int RANK2, typename = std::enable_if_t<(RANK1 != RANK2), bool>> | |
| bool | operator!= (TensorIndices< RANK1 > const &a, TensorIndices< RANK2 > const &b) |
| Comparison operator with tensors of different rank. More... | |
| template<typename... DIMS> | |
| auto | makeTensorIndices (DIMS...dims) |
| Instantiates a TensorIndices class with the specified dimensions. More... | |
| template<template< typename T, typename... > class Extractor, typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| auto | getByExtractedType (Tuple const &data) -> decltype(auto) |
| Returns the value of the element containing the specified type. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename T > | |
| auto | makeTagged (T &obj) -> decltype(auto) |
"Converts" obj to an object with tag Tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename T > | |
| auto | makeTagged (T const &obj) -> decltype(auto) |
"Converts" obj to an object with tag Tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename T > | |
| auto | makeTagged (T const &&obj) -> decltype(auto) |
"Converts" obj to an object with tag Tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename T > | |
| auto | makeTagged (T &&obj) -> decltype(auto) |
"Converts" obj to an object with tag Tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tagged > | |
| auto | removeTag (Tagged &tagged) -> decltype(auto) |
| "Converts" a tagged type back to its original type. More... | |
| template<typename Tagged > | |
| auto | removeTag (Tagged const &tagged) -> decltype(auto) |
| "Converts" a tagged type back to its original type. More... | |
| template<typename Tagged > | |
| auto | removeTag (Tagged const &&tagged) -> decltype(auto) |
| "Converts" a tagged type back to its original type. More... | |
| template<typename Tagged > | |
| auto | removeTag (Tagged &&tagged) -> decltype(auto) |
| "Converts" a tagged type back to its original type. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| auto | getByTag (Tuple const &data) -> decltype(auto) |
| Returns the object with the specified tag. More... | |
| template<typename _Key , typename _Tp , typename _Compare > | |
| bool | operator== (const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__x, const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__y) |
| template<typename _Key , typename _Tp , typename _Compare > | |
| bool | operator< (const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__x, const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__y) |
| template<typename _Key , typename _Tp , typename _Compare > | |
| bool | operator!= (const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__x, const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__y) |
| Based on operator==. More... | |
| template<typename _Key , typename _Tp , typename _Compare > | |
| bool | operator> (const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__x, const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__y) |
| Based on operator<. More... | |
| template<typename _Key , typename _Tp , typename _Compare > | |
| bool | operator<= (const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__x, const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__y) |
| Based on operator<. More... | |
| template<typename _Key , typename _Tp , typename _Compare > | |
| bool | operator>= (const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__x, const VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__y) |
| Based on operator<. More... | |
| template<typename _Key , typename _Tp , typename _Compare > | |
| void | swap (VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__x, VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare > &__y) |
| See VectorMap::swap(). More... | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, EventChangeTracker_t const &trk) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, DataProductChangeTracker_t const &trk) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, PlaneDataChangeTracker_t const &trk) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | staticDumpClassName () |
| Helper to determine the type of a variable at compilation time. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | staticDumpClassName (T) |
| Helper to determine the type of a variable at compilation time. More... | |
| template<typename A , typename B > | |
| constexpr auto | absDiff (A const &a, B const &b) |
| Returns the absolute value of the difference between two values. More... | |
| template<typename PRODUCER , typename T , typename U , typename D > | |
| bool | CreateAssnD (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, art::Assns< T, U, D > &assn, size_t first_index, size_t second_index, typename art::Assns< T, U, D >::data_t &&data) |
| Creates a single one-to-one association with associated data. More... | |
| template<typename PRODUCER , typename T , typename U , typename D > | |
| bool | CreateAssnD (PRODUCER const &prod, art::Event &evt, art::Assns< T, U, D > &assn, size_t first_index, size_t second_index, typename art::Assns< T, U, D >::data_t const &data) |
| Creates a single one-to-one association with associated data. More... | |
Variables | |
| template<typename > | |
| constexpr bool | always_false_v = false |
| A templated constant, always false. More... | |
| template<typename > | |
| constexpr bool | always_true_v = true |
| A template constant always true. More... | |
| constexpr double | kGeVToElectrons = 4.237e7 |
| 23.6eV per ion pair, 1e9 eV/GeV More... | |
| constexpr double | kc = 29.9792458 |
| Speed of light in vacuum in LArSoft units [cm/ns]. More... | |
| constexpr double | kMeterToCentimeter = 1.e2 |
| 1 m = 100 cm More... | |
| constexpr double | kCentimeterToMeter = 1./kMeterToCentimeter |
| constexpr double | kMeterToKilometer = 1.e-3 |
| 1000 m = 1 km More... | |
| constexpr double | kKilometerToMeter = 1./kMeterToKilometer |
| constexpr double | keVToMeV = 1.e-6 |
| 1e6 eV = 1 MeV More... | |
| constexpr double | kMeVToeV = 1./keVToMeV |
| constexpr double | kBogusD = -999. |
| obviously bogus double value More... | |
| constexpr int | kBogusI = -999 |
| obviously bogus integer value More... | |
| constexpr float | kBogusF = -999. |
| obviously bogus float value More... | |
| constexpr double | quietCompiler = kBogusD*kBogusI*kBogusF*kRecombA*kRecombk*kGeVToElectrons |
| const double | kINVALID_DOUBLE = std::numeric_limits<Double_t>::max() |
| constexpr RangeForWrapperTag | range_for |
| template<template< typename T, typename... > class Extractor, typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr std::size_t | index_of_extracted_type_v = index_of_extracted_type<Extractor, Target, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in index_of_extracted_type. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr std::size_t | index_of_type_v = index_of_type<Target, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in index_of_type. More... | |
| template<template< typename T, typename... > class Extractor, typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr bool | has_extracted_type_v = has_extracted_type<Extractor, Target, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in has_extracted_type. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr bool | has_type_v = has_type<Target, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in has_type. More... | |
| template<template< typename T, typename... > class Extractor, typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr bool | has_duplicate_extracted_types_v = has_duplicate_extracted_types<Extractor, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in has_duplicate_extracted_types. More... | |
| template<typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr bool | has_duplicate_types_v = has_duplicate_types<Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in has_duplicate_types. More... | |
| template<template< typename T, typename... > class Extractor, typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr unsigned int | count_extracted_types_v = count_extracted_types<Extractor, Target, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in count_extracted_types. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr unsigned int | count_types_v = count_types<Target, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in count_extracted_types. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr std::size_t | index_of_tag_v = index_of_tag<Tag, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in index_of_tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr bool | has_tag_v = has_tag<Tag, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in has_tag. More... | |
| template<typename Tag , typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr unsigned int | count_tags_v = count_tags<Tag, Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in count_tags. More... | |
| template<typename Tuple > | |
| constexpr bool | has_duplicate_tags_v = has_duplicate_tags<Tuple>() |
Direct access to the value in has_duplicate_tags. More... | |
| const float | SQRT_TWO_PI = 2.506628 |
Recombination factor coefficients (NIM). | |
Recombination factor coefficients come from Nucl.Instrum.Meth.A523:275-286,2004
| |
| constexpr double | kRecombA = 0.800 |
| A constant. More... | |
| constexpr double | kRecombk = 0.0486 |
Recombination factor coefficients (modified box, ArguNeuT JINST). | |
Recombination factor coefficients come from Nucl.Instrum.Meth.A523:275-286,2004
| |
| constexpr double | kModBoxA = 0.930 |
| Modified Box Alpha. More... | |
| constexpr double | kModBoxB = 0.212 |
| Modified Box Beta in g/(MeV cm²)*kV/cm. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename... T> | |
| using | count_type_in_list = details::count_type_in_list_impl< Target, T... > |
Returns how many of the types in T exactly match Target. More... | |
| template<std::size_t N, typename... T> | |
| using | typelist_element_type = std::tuple_element< N, std::tuple< T... >> |
Returns the N type of the type list. More... | |
| template<std::size_t N, typename... T> | |
| using | typelist_element_t = typename typelist_element_type< N, T... >::type |
Direct access to the value in typelist_element_type. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename... T> | |
| using | type_is_in = details::type_is_in_impl< Target, T... > |
Holds whether the Target type is among the ones in the T pack. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename... T> | |
| constexpr unsigned int | count_type_in_list_v = count_type_in_list<Target, T...>() |
Direct access to the value in count_type_in_list. More... | |
| template<typename Target , typename... T> | |
| constexpr bool | type_is_in_v = type_is_in<Target, T...>() |
Direct access to the value in type_is_in. More... | |
Namespace for general, non-LArSoft-specific utilities.
Namespace for general, not LArSoft-specific utilities.
General LArSoft Utilities.
Generic namespace of utility functions generally independent of LArSoft.
Title: PIDA Algorithim Class Author: Wes Ketchum (wketchum@lanl.gov), based on ideas/code from Bruce Baller
Description: Algorithm that calculates the PIDA from a calorimetry object Input: anab::Calorimetry Output: PIDA information
Some physical constants are also included here. As a reminder, the "standard" units in LArSoft are:
SumSecondFunction 28-Jul-2009 William Seligman seligman@nevis.columbia.edu When using STL, maps, and the std::accumulate function, there's one function I keep coding over and over again: accumulate the second member of a pair.
To save myself time (and others who know and use STL), here's a complete STL-compatible implementation of that function. To use it, assume you have an object:
std::map<K,V> myMap;
To sum all the V's in the map:
V sum = std::accumulate( myMap.begin(),myMap.end(),V(),SumSecondFunction<K,V>() );
(Yes, I know there are other, better ways to do this, if one has access to BOOST. Unfortunately, we're not supposed to use BOOST in LArSoft, since as of Jul-2009 it's not universally installed on FNAL machines.)
VectorMap 17-Apr-2008 William Seligman seligman@nevis.columbia.edu
This class is an implementation of a concept discussion in "Effective STL" by Scott Meyers:
STL maps are useful because their contents are always sorted, so they're effective for fast searches. However, in almost every other respect vectors are superior: They take up less space, and they use random-access iterators.
This class implements "sorted vector maps," that is, an STL-style map implemented as a sorted STL vector of pairs. I've done my best to implement all aspects of the std::map interface in this class, with some additions; if you've defined the following:
VectorMap<key_type, data_type> svm;
INCREDIBLY IMPORTANT NOTE: The "key type" of a VectorMap cannot be a "const" type (unlike maps); it won't even compile. When you do an insert, the underlying vector has to move things around within its list, and it uses the assignment operator=() (or "vector{i+1)=vector(i)" if you like). You can't do that if either the key or the data is const.
As with a map, there's no way to insert items at a specific location in a VectorMap. The insertion methods (including operator[]) all operate on a sorted sequence according to the key. Because of this, insertions take a long time.
However, for our processing, this doesn't matter much; for almost all our maps, we typically have:
For this usage, a sorted vector is generally superior to a map.
This class just implements the equivalent of an STL map, not a multimap, set, nor a multiset. If there's a need, I may create additional classes.
Is there any map feature that's not implemented? Yes:
Advanced implementation note: Depending on the application, it might be possible to speed up this class by using "lazy evaluation"; that is, we wouldn't actually sort the vector until the user actually tries to access its contents. I'm not going to do this, because:
A) I don't think my programming skills are up to the task.
B) In the primary application for which I plan to use this class (Monte-Carlo particle tracks), we're performing at least one search after every insert; lazy evaluation wouldn't be much of a speed improvement.
Feb-2011 WGS: VectorMap mostly looks like a map, but there are some memory-management issues that relate to it being a vector. Include the vector-based routines reserve() and capacity().
Title: GaussianEliminationAlg Class Author: Wes Ketchum (wketchum@lanl.gov)
Description: Class that solves system of linear equations via Gaussian Elimination. Intended for use with RFFHitFitter
| using util::GridContainer2D = typedef GridContainerBase2D<DATUM, GridContainer2DIndices> |
Container allowing 2D indexing.
| DATUM | type of contained data |
This is an alias for GridContainerBase2D, with a proper index manager. See the documentation of GridContainerBase2D.
Definition at line 267 of file GridContainers.h.
| using util::GridContainer2DIndices = typedef GridContainerIndicesBase2D<> |
Index manager for a container of data arranged on a 2D grid.
Definition at line 181 of file GridContainerIndices.h.
| using util::GridContainer3D = typedef GridContainerBase3D<DATUM, GridContainer3DIndices> |
Container allowing 3D indexing.
| DATUM | type of contained data |
This is an alias for GridContainerBase3D, with a proper index manager. See the documentation of GridContainerBase3D.
Definition at line 279 of file GridContainers.h.
| using util::GridContainer3DIndices = typedef GridContainerIndicesBase3D<> |
Index manager for a container of data arranged on a 3D grid.
Definition at line 184 of file GridContainerIndices.h.
| using util::LArPropertiesArgoNeuT = typedef LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT |
type of provider name following LArSoft name convention
Definition at line 235 of file LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT.h.
| using util::MatrixIndices = typedef TensorIndices<2U> |
Type for indexing a 2D-tensor (matrix)
Definition at line 550 of file TensorIndices.h.
| typedef std::map< UBDaqID, UBLArSoftCh_t > util::UBChannelMap_t |
Definition at line 48 of file DatabaseUtil.h.
| typedef std::map< UBLArSoftCh_t, UBDaqID > util::UBChannelReverseMap_t |
Definition at line 49 of file DatabaseUtil.h.
| typedef int util::UBLArSoftCh_t |
Definition at line 46 of file DatabaseUtil.h.
| constexpr auto util::absDiff | ( | A const & | a, |
| B const & | b | ||
| ) |
Returns the absolute value of the difference between two values.
| A | type of the first value |
| B | type of the second value (must actually be as A) |
| a | the first value |
| b | the second value |
a and bThe pecularity of this implementation is that it always avoids taking the difference between the smallest and the largest of a and b. An equivalent implementation is:
It still assumes that the difference is representable in A; for example, this assumption will fail for int types with a a very large number and b a very small (i.e. negative) number.
Requirements:
A and B must be the same type Definition at line 43 of file NumericUtils.h.
Referenced by cluster::ClusterCrawlerAlg::AddHit(), cluster::ClusterCrawlerAlg::ClusterHitsOK(), cluster::DBScan3DAlg::init(), AcceptFindNeighbors::isNear(), calo::Calorimetry::produce(), pma::ProjectionMatchingAlg::selectInitialHits(), and cluster::ClusterCrawlerAlg::Vtx3ClusterMatch().
| auto util::associated_groups | ( | A const & | assns | ) |
Helper functions to access associations in order.
| A | type of association being read |
| assns | the association being read |
This function provides a functionality equivalent to art::for_each_group(), but it grants the caller additional control on the external loop and on the function.
Example: assuming that a module with input tag stored in fTrackTag has created associations of each track to its hits, the total charge for each track can be extracted by:
A number of important points need to be realised about this example:
art::for_each_group()hits is an object representing a range of art pointers (art::Ptr<recob::Hit>) which can be navigated with the begin()/end() free functions, or in a range-for loop;util::associated_groups_with_left() instead. Definition at line 94 of file ForEachAssociatedGroup.h.
References a1, a2, and range_for.
Referenced by TrackProducerFromTrack::produce(), TrackProducerFromTrackTrajectory::produce(), and TrackProducerFromPFParticle::produce().
| auto util::associated_groups_with_left | ( | A const & | assns | ) |
Helper functions to access associations in order, also with key.
| A | type of association being read |
| assns | the association being read |
This function provides a functionality equivalent to art::for_each_group_with_left(), but it grants the caller additional control on the external loop and on the function.
Example: assuming that a module with input tag stored in fTrackTag has created associations of each track to its hits, the total charge for each track can be extracted by:
A number of important points need to be realised about this example:
art::for_each_group_with_left()hits is an object representing a range of art pointers (art::Ptr<recob::Hit>) which can be navigated with the begin()/end() free functions, or in a range-for loop. Definition at line 152 of file ForEachAssociatedGroup.h.
References a1, a2, and range_for.
| bool util::CreateAssn | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| std::vector< T > const & | a, | ||
| art::Ptr< U > const & | b, | ||
| art::Assns< U, T > & | assn, | ||
| std::string | a_instance, | ||
| size_t | indx = UINT_MAX |
||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-one association.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the object already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| a | vector of data products that are in, or will be put into, evt |
| b | art::Ptr to the (new) object to be associated to the one in a |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| a_instance | name of the instance that will be used for a in evt |
| indx | index of the element in a to be associated with b (default: the last element) |
As example of usage: create a wire/raw digit association. This code should live in the art::EDProduce::produce() method. The raw::RawDigit product was created already by a DigitModuleLabel module. The code is supposed to produce one recob::Wire for each existing raw::RawDigit, and contextually associate the new wire to the source digit. We are also assuming that there might be different RawDigit sets produced by the same producer: we identify the one we care of by the string spill_name and we create wires and associations with the same label for convenience.
// this is the original list of digits, thawed from the event
art::Handle< std::vector<raw::RawDigit>> digitVecHandle;
evt.getByLabel(DigitModuleLabel, spill_name, digitVecHandle);
// the collection of wires that will be written as data product
std::unique_ptr<std::vector<recob::Wire>> wirecol(new std::vector<recob::Wire>);
// ... and an association set
std::unique_ptr<art::Assns<raw::RawDigit,recob::Wire>> WireDigitAssn
(new art::Assns<raw::RawDigit,recob::Wire>);
for(size_t iDigit = 0; iDigit < digitVecHandle->size(); ++iDigit) {
// turn the digit into a art::Ptr:
art::Ptr<raw::RawDigit> digit_ptr(digitVecHandle, iDigit);
// store the wire in its final position in the data product;
// the new wire is currently the last of the list
wirecol->push_back(std::move(wire));
// add an association between the last object in wirecol
// (that we just inserted) and digit_ptr
if (!util::CreateAssn(*this, evt, *wirecol, digit_ptr, *WireDigitAssn, spill_name)) {
throw art::Exception(art::errors::ProductRegistrationFailure)
<< "Can't associate wire #" << (wirecol->size() - 1)
<< " with raw digit #" << digit_ptr.key();
} // if failed to add association
} // for digits
evt.put(std::move(wirecol), spill_name);
evt.put(std::move(WireDigitAssn), spill_name);
Definition at line 591 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), e, and art::Event::productGetter().
Referenced by cluster::ClusterMergeHelper::AppendResult(), CreateAssn(), lar_cluster3d::Cluster3D::findTrackSeeds(), lar_cluster3d::Cluster3D::ArtOutputHandler::makeClusterHitAssns(), lar_cluster3d::Cluster3D::ArtOutputHandler::makePFPartClusterAssns(), lar_cluster3d::Cluster3D::ArtOutputHandler::makePFPartEdgeAssns(), lar_cluster3d::Cluster3D::ArtOutputHandler::makePFPartPCAAssns(), lar_cluster3d::Cluster3D::ArtOutputHandler::makePFPartSeedAssns(), lar_cluster3d::Cluster3D::ArtOutputHandler::makePFPartSpacePointAssns(), wc::MergeWireCell::MakeShowers(), lar_cluster3d::Cluster3D::ArtOutputHandler::makeSpacePointHitAssns(), wc::MergeWireCell::MakeTracks(), vertex::AggregateVertex::MatchV2T(), event::EventMaker::produce(), opdet::FlashClusterMatch::produce(), lar_pandora::LArPandoraTrackCreation::produce(), lar_pandora::LArPandoraShowerCreation::produce(), trk::TrackContainmentTagger::produce(), vertex::VertexCheater::produce(), trkf::TCTrack::produce(), cluster::SimpleClusterMerger::produce(), event::EventCheater::produce(), shwf::ShowerCheater::produce(), opdet::BeamFlashCompatabilityCheck::produce(), trkf::SpacePointCheater::produce(), trkf::SpacePointFinder::produce(), cluster::LineCluster::produce(), sim::MergeSimSources::produce(), tss::TrackShowerHits::produce(), sppt::TTSpacePointFinder::produce(), cluster::SimpleLineCluster::produce(), trkf::BezierTrackerModule::produce(), trkf::TrackCheater::produce(), cluster::ClusterCheater::produce(), calo::BezierCalorimetry::produce(), pid::Chi2ParticleID::produce(), calo::TrackCalorimetry::produce(), cosmic::BeamFlashTrackMatchTagger::produce(), caldata::CalWire::produce(), cluster::DBCluster3D::produce(), wc::MergeWireCell::produce(), opdet::OpFlashFinder::produce(), cluster::TrajCluster::produce(), caldata::CalWireT962::produce(), cluster::DBcluster::produce(), cluster::FuzzyClusterMerger::produce(), cosmic::TrackPFParticleMatch::produce(), ShowerReco3D::produce(), cluster::LineMerger::produce(), cluster::BlurredClustering::produce(), cluster::ClusterCrawler::produce(), cluster::fuzzyCluster::produce(), trkf::SpacePts::produce(), cosmic::CosmicPFParticleTagger::produce(), shower::EMShower::produce(), trkf::Track3Dreco::produce(), cosmic::CosmicTrackTagger::produce(), trkf::TrackKalmanCheater::produce(), vertex::VertexMatch::produce(), shower::TCShower::produce(), shwf::ShowerFinder::produce(), cosmic::CosmicPCAxisTagger::produce(), cosmic::CosmicClusterTagger::produce(), trkf::CCTrackMaker::produce(), vertex::PrimaryVertexFinder::produce(), cluster::SmallClusterFinder::produce(), vertex::HarrisVertexFinder::produce(), cluster::EndPointModule::produce(), trkf::TrackStitcher::produce(), ems::EMShower3D::produce(), cluster::HoughLineFinder::produce(), calo::Calorimetry::produce(), vertex::VertexFinder2D::produce(), shwf::ShowerReco::produce(), trkf::Track3DKalman::produce(), evgen::GENIEGen::produce(), lbne::PhotonCounterT0Matching::produce(), trkf::PMAlgTrajFitter::produce(), trkf::Track3DKalmanSPS::produce(), t0::MCTruthT0Matching::produce(), evd::GraphCluster::produce(), trkf::PMAlgTrackMaker::produce(), trkf::CosmicTracker::produce(), evgen::MarleyTimeGen::produce(), ems::MergeEMShower3D::produce(), mvapid::MVAAlg::RunPID(), opdet::TrackTimeAssoc::StoreFlashMatches(), and lar_pandora::LArPandoraEvent::WriteAssociation().
|
inline |
Creates a single one-to-one association.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the object already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| a | vector of data products that are in, or will be put into, evt |
| b | art::Ptr to the (new) object to be associated to the one in a |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| indx | index of the element in a to be associated with b (default: the last element) |
The instance name of the product a will be in is assumed empty. Example of usage:
// this is the original list of digits, thawed from the event
art::Handle< std::vector<raw::RawDigit>> digitVecHandle;
evt.getByLabel(DigitModuleLabel, digitVecHandle);
// the collection of wires that will be written as data product
std::unique_ptr<std::vector<recob::Wire>> wirecol(new std::vector<recob::Wire>);
// ... and an association set
std::unique_ptr<art::Assns<raw::RawDigit,recob::Wire>> WireDigitAssn
(new art::Assns<raw::RawDigit,recob::Wire>);
for(size_t iDigit = 0; iDigit < digitVecHandle->size(); ++iDigit) {
// turn the digit into a art::Ptr:
art::Ptr<raw::RawDigit> digit_ptr(digitVecHandle, iDigit);
// store the wire in its final position in the data product;
// the new wire is currently the last of the list
wirecol->push_back(std::move(wire));
// add an association between the last object in wirecol
// (that we just inserted) and digit_ptr
if (!util::CreateAssn(*this, evt, *wirecol, digit_ptr, *WireDigitAssn)) {
throw art::Exception(art::errors::ProductRegistrationFailure)
<< "Can't associate wire #" << (wirecol->size() - 1)
<< " with raw digit #" << digit_ptr.key();
} // if failed to add association
} // for digits
evt.put(std::move(wirecol));
evt.put(std::move(WireDigitAssn));
Definition at line 213 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References CreateAssn(), CreateAssnD(), tca::evt, FindUNotAssociatedToT(), FindUNotAssociatedToTP(), GetAssociatedVectorManyI(), GetAssociatedVectorManyP(), GetAssociatedVectorOneI(), GetAssociatedVectorOneP(), geo::vect::indices(), and lar::dump::vector().
| bool util::CreateAssn | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| art::Ptr< T > const & | a, | ||
| art::Ptr< U > const & | b, | ||
| art::Assns< U, T > & | assn | ||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-one association.
| T | type of one object to associate |
| U | type of the other object to associate |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| a | art::Ptr to the first object in the association |
| b | art::Ptr to the object to be associated to the one in a |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
This is the simplest way ever. Neither the event not the producer references are used.
Definition at line 621 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), and e.
| bool util::CreateAssn | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| std::vector< T > const & | a, | ||
| art::PtrVector< U > const & | b, | ||
| art::Assns< T, U > & | assn, | ||
| size_t | indx = UINT_MAX |
||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-many association.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the many objects already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| a | vector of data products that are in, or will be put into, evt |
| b | art::PtrVector to the (new) objects to be associated to the one in a |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| indx | index of the element in a to be associated with all the ones in b (default: the last element) |
A "one-to-many" association is actually a number of one-to-one associations. If you want to keep the information of the order of the many, you may have to use an association with a data member (the third template parameter that we pretent not to exist).
Definition at line 645 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), e, and art::Event::productGetter().
| bool util::CreateAssn | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| art::Ptr< T > const & | a, | ||
| std::vector< art::Ptr< U >> const & | b, | ||
| art::Assns< T, U > & | assn | ||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-many association.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the many objects already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| a | art::Ptr to the item to be associated with many |
| b | vector to art::Ptr to the (new) objects to be associated to a |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
A "one-to-many" association is actually a number of one-to-one associations. If you want to keep the information of the order of the many, you may have to use an association with a data member (the third template parameter that we pretent not to exist).
Definition at line 672 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), and e.
| bool util::CreateAssn | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| std::vector< T > const & | a, | ||
| std::vector< art::Ptr< U >> const & | b, | ||
| art::Assns< T, U > & | assn, | ||
| size_t | indx = UINT_MAX |
||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-many association.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the many objects already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| a | vector of data products that are in, or will be put into, evt |
| b | vector to art::Ptr to the (new) objects to be associated to the one in a |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| indx | index of the element in a to be associated with all the ones in b (default: the last element) |
A "one-to-many" association is actually a number of one-to-one associations. If you want to keep the information of the order of the many, you may have to use an association with a data member (the third template parameter that we pretent not to exist).
Definition at line 695 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), e, and art::Event::productGetter().
| bool util::CreateAssn | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| std::vector< T > const & | a, | ||
| std::vector< U > const & | b, | ||
| art::Assns< T, U > & | assn, | ||
| size_t | startU, | ||
| size_t | endU, | ||
| size_t | indx = UINT_MAX |
||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-many association.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the many objects already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| a | vector of data products that are in, or will be put into, evt |
| b | vector of the (new) objects to be associated to the one in a |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| startU | index in b of the first element to be associated to the one in a |
| endU | index in b after the last element to be associated to the one in a |
| indx | index of the element in a to be associated with all the ones in b (default: the last element) |
Use this when the objects in b are not yet stored in the event and are in a std::vector collection instead.
The method gets the product id for those as well as for the element in a. Also specify the range of entries to use from the std::vector collection of U objects.
A "one-to-many" association is actually a number of one-to-one associations. If you want to keep the information of the order of the many, you may have to use an association with a data member (the third template parameter that we pretent not to exist).
Definition at line 723 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), e, and art::Event::productGetter().
| bool util::CreateAssn | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| std::vector< T > const & | a, | ||
| std::vector< U > const & | b, | ||
| art::Assns< T, U > & | assn, | ||
| std::vector< size_t > const & | indices, | ||
| size_t | indx = UINT_MAX |
||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-many association.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the many objects already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| a | vector of data products that are in, or will be put into, evt |
| b | vector of the (new) objects to be associated to the one in a |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| indices | indices of the elements in b to be associated to the one in a |
| indx | index of the element in a to be associated with all the ones in b (default: the last element) |
Use this when the objects in b are not yet stored in the event and are in a std::vector collection instead.
The method gets the product id for those as well as for the element in a. Also specify the entries to use from the std::vector collection of U objects.
A "one-to-many" association is actually a number of one-to-one associations. If you want to keep the information of the order of the many, you may have to use an association with a data member (the third template parameter that we pretent not to exist).
Definition at line 758 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), e, and art::Event::productGetter().
| bool util::CreateAssn | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| art::Assns< T, U > & | assn, | ||
| size_t | first_index, | ||
| Iter | from_second_index, | ||
| Iter | to_second_index | ||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-many association.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the many objects already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| Iter | iterator to size_t-compatible elements |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| first_index | index of the object of type T to be associated to all the others |
| from_second_index | iterator pointing to the first of the indices of U type objects to be associated to the one of the first type |
| to_second_index | iterator pointing after the last of the indices of U type objects to be associated to the one of the first type |
A "one-to-many" association is actually a number of one-to-one associations. If you want to keep the information of the order of the many, you may have to use an association with a data member (the third template parameter that we pretent not to exist).
Use this if the objects that have to be associated to the one of type T are sparse, spread across a to-be-data-product, but you have a list of the indices in the data product of the elements to associate to the one of type T. In other words, given that you have a data product "a" of type std::vector<T> and a data product "b" of type std::vector<U>, this method creates an association betweena[first_index]and b[*(from_second_index)], another between a[first_index] and b[*(from_second_index + 1)], etc.
The surprising concept here is that you don't need to specify neither of the collections of T or U elements. The data product is uniquely defined by its type, producer, process and product label. Here we assume that the type of the products are std::vector<T> and std::vector<U>, and that the products have empty product labels, and that the producer is prod for both of them.
Definition at line 792 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), e, and art::Event::productGetter().
| bool util::CreateAssnD | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| art::Assns< T, U, D > & | assn, | ||
| size_t | first_index, | ||
| size_t | second_index, | ||
| typename art::Assns< T, U, D >::data_t && | data | ||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-one association with associated data.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the many objects already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| D | type of the "metadata" coupled to this pair association |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| first_index | index of the object of type T to be associated |
| second_index | index of the object of type U to be associated |
| data | "metadata" to be store in this association |
Use this if you want some metadata to travel together with the association. An example may be the order of the second element within a list:
size_t a_index = 2;
std::vector<size_t> b_indices{ 6, 9, 18, 12 };
for (size_t i = 0; i < b_indices.size(); ++i)
CreateAssn(prod, evt, assn, a_index, b_index[i], i);
In this way, the association between the element #2 of "a" (a vector that is not specified – nor needed – in this snippet of code) and the element #18 will be remembered as being the third (metadata value of 2). In this example metadata is of type size_t the association would be declared as art::Assn<A, B, size_t>. A FindMany query of that association might look like:
art::Handle<std::vector<A>> a_list; // read this from the event
art::FindMany<B, size_t> Query(a_list, event, ModuleLabel);
// search for the last of the objects associated to the third element:
size_t a_index = 2; // this means third element
std::vector<size_t const*> const& metadata = Query.data(a_index);
size_t largest_index = 0, last_item = 0;
for (size_t iB = 0; iB < metadata.size(); ++iB) {
if (largest_index >= *(metadata[iB])) continue;
largest_index = *(metadata[iB]);
last_item = iB;
} // for iB
B const& lastB = Query.at(last_item);
In alternative, the elements and their metadata can be fetched simultaneously with:
std::vector<art::Ptr<B>> const& Bs; std::vector<size_t const*> const& metadata; size_t a_index = 2; // this means third element size_t nMatches = Query.get(a_index, Bs, metadata);
Definition at line 836 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), e, and art::Event::productGetter().
Referenced by CreateAssn(), cluster::LineCluster::produce(), cluster::TrajCluster::produce(), and cluster::ClusterCrawler::produce().
| bool util::CreateAssnD | ( | PRODUCER const & | prod, |
| art::Event & | evt, | ||
| art::Assns< T, U, D > & | assn, | ||
| size_t | first_index, | ||
| size_t | second_index, | ||
| typename art::Assns< T, U, D >::data_t const & | data | ||
| ) |
Creates a single one-to-one association with associated data.
| T | type of the new object to associate |
| U | type of the many objects already in the data product or art::Ptr |
| D | type of the "metadata" coupled to this pair association |
| prod | reference to the producer that will write the vector a |
| evt | reference to the current event |
| assn | reference to association object where the new one will be put |
| first_index | index of the object of type T to be associated |
| second_index | index of the object of type U to be associated |
| data | "metadata" to be store in this association |
Use this if you want some metadata to travel together with the association. An example may be the order of the second element within a list:
size_t a_index = 2;
std::vector<size_t> b_indices{ 6, 9, 18, 12 };
for (size_t i = 0; i < b_indices.size(); ++i)
CreateAssn(prod, evt, assn, a_index, b_index[i], i);
In this way, the association between the element #2 of "a" (a vector that is not specified – nor needed – in this snippet of code) and the element #18 will be remembered as being the third (metadata value of 2). In this example metadata is of type size_t the association would be declared as art::Assn<A, B, size_t>. A FindMany query of that association might look like:
art::Handle<std::vector<A>> a_list; // read this from the event
art::FindMany<B, size_t> Query(a_list, event, ModuleLabel);
// search for the last of the objects associated to the third element:
size_t a_index = 2; // this means third element
std::vector<size_t const*> const& metadata = Query.data(a_index);
size_t largest_index = 0, last_item = 0;
for (size_t iB = 0; iB < metadata.size(); ++iB) {
if (largest_index >= *(metadata[iB])) continue;
largest_index = *(metadata[iB]);
last_item = iB;
} // for iB
B const& lastB = Query.at(last_item);
In alternative, the elements and their metadata can be fetched simultaneously with:
std::vector<art::Ptr<B>> const& Bs; std::vector<size_t const*> const& metadata; size_t a_index = 2; // this means third element size_t nMatches = Query.get(a_index, Bs, metadata);
Definition at line 873 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::addSingle(), e, and art::Event::productGetter().
|
inline |
Converts the argument angle from degrees into radians.
Definition at line 84 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by cluster::LazyClusterParamsAlg::StartAngle(), and cluster::StandardClusterParamsAlg::StartAngle().
| void util::DumpAssociationsIntro | ( | Stream && | out, |
| art::Assns< Left, Right, Data > const & | assns | ||
| ) |
Dumps a short introduction about specified association.
| Stream | type of output stream |
| Left | first type in the association |
| Right | second type in the association |
| Data | metadata type in the association |
| out | output stream |
| assns | the associations to be dumped |
Definition at line 33 of file DumpAssociations.h.
References art::Assns< L, R, D >::size().
| auto util::filterRangeFor | ( | Range && | range, |
| Pred && | pred | ||
| ) | -> decltype(auto) |
Provides iteration only through elements passing a condition.
| Range | the data to be iterated |
| Pred | the type of the predicate to be fulfilled |
| range | the data to be iterated through |
| pred | the predicate to be tested |
This adapter makes the range for loop iterate only through the elements of range which fulfil the predicate pred.
This example will print: "0 3 6 9 ":
Note that pred may be copied (range will not be).
Range is an object which can itself go through a range-for:
for (auto&& v: range);
is valid
Pred is a copiable unary function type, whose single argument can be converted from the value type of Range, and whose return value can be converted into a bool vaule Definition at line 137 of file filterRangeFor.h.
Referenced by proxy::TrackCollectionProxyElement< CollProxy >::selectPoints().
|
inline |
Definition at line 911 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References fa(), and art::Ptr< T >::get().
Referenced by CreateAssn().
|
inline |
Definition at line 936 of file AssociationUtil.h.
References fa().
Referenced by CreateAssn().
| void util::for_each_associated_group | ( | A const & | assns, |
| F & | func | ||
| ) |
Helper functions to access associations in order.
| A | type of association being read |
| F | type of functor to be called on each associated group |
| assns | the association being read |
| func | functor to be called on each associated group |
art::for_each_group(). Definition at line 49 of file ForEachAssociatedGroup.h.
References art::for_each_group().
|
inline |
Definition at line 980 of file AssociationUtil.h.
Referenced by microboone::CosmicRemovalAna::analyze(), CreateAssn(), calo::TrackCalorimetry::produce(), and cosmic::BeamFlashTrackMatchTagger::produce().
|
inline |
Definition at line 989 of file AssociationUtil.h.
Referenced by CreateAssn().
|
inline |
Definition at line 962 of file AssociationUtil.h.
Referenced by CreateAssn().
|
inline |
Definition at line 971 of file AssociationUtil.h.
Referenced by microboone::CosmicRemovalAna::analyze(), and CreateAssn().
| auto util::groupByIndex | ( | Groups && | groups, |
| std::size_t | index | ||
| ) | -> decltype(auto) |
Returns the group within groups with the specified index.
| Groups | the type of collection of groups |
| groups | the collection of all groups |
| index | the index of the group to be accessed |
associated_groups()The groups argument is expected to be the one returned by associated_groups.
Definition at line 180 of file ForEachAssociatedGroup.h.
Referenced by TrackProducerFromPFParticle::produce().
| std::vector<size_t> util::MakeIndex | ( | Coll const & | data, |
| KeyOf | key_of = KeyOf() |
||
| ) |
Creates a map of indices from an existing collection.
| Coll | type of the collection |
| KeyOf | type of the extractor of the key |
| data | the data collection |
| key_of | instance of a functor extracting a key value from a datum |
This function maps the index of the items in data to an integral key extracted from each item. For example, if the items are wires and the key_of function extracts their channel ID, the resulting vector will contain for each channel ID the index in data of the wire with that channel ID.
The key is converted into a unsigned integer (size_t). If multiple items have the same key, the outcome for that key is undefined. If no items has a specific key, the index of that key is assigned as
, i.e. an index larger than the size of the original data collection.
The returned vector is big enough to accommodate indices corresponding to the keys of all the items in data. It may contain "holes" (that is, some keys that have no corresponding items have a
value). The memory allocated for the vector may be larger than necessary (if that is a problem, std::vector::shrink_to_fit() can be used, but it may create more problems than it solves).
Definition at line 43 of file MakeIndex.h.
References max.
Referenced by recob::HitCollectionAssociator::prepare_associations().
| auto util::MakeMap | ( | Coll const & | data, |
| KeyOf | key_of = KeyOf() |
||
| ) | -> std::vector<decltype(key_of(*(data.begin()))) const*> |
Creates a map of objects from an existing collection.
| Coll | type of the collection |
| KeyOf | type of the extractor of the key |
| data | the data collection |
| key_of | instance of a functor extracting a key value from a datum |
This function maps the items in data to an integral key extracted from each of them. For example, if the items are wires and the key_of function extracts their channel ID, the resulting vector will contain for each channel ID the pointer to the wire with that channel ID.
The key is converted into a unsigned integer (size_t). If multiple items have the same key, the outcome for that key is undefined. If no items has a specific key, the index of that key is assigned a null pointer.
The returned vector is big enough to accommodate pointers corresponding to the keys of all the items in data. It may contain "holes" (that is, some keys that have no corresponding items have a null pointer value). The memory allocated for the vector may be larger than necessary (if that is a problem, std::vector::shrink_to_fit() can be used, but it may create more problems than it solves).
Definition at line 99 of file MakeIndex.h.
References max.
| auto util::makePointerVector | ( | Coll & | coll | ) |
Creates a STL vector with pointers to data from another collection.
| Coll | type of collection of data |
| coll | data collection |
coll data elements, with same order Definition at line 103 of file SortByPointers.h.
References n.
Referenced by SortByPointers().
| auto util::makeTensorIndices | ( | DIMS... | dims | ) |
Instantiates a TensorIndices class with the specified dimensions.
| DIMS | types for each of the arguments |
| dims | size of each of the dimensions |
The rank of the tensor is determined by the number of arguments; example:
will initialise a TensorIndices<2> (that's matrix indices), for a 3 x 4 (3 rows, 4 columns) disposition.
Definition at line 542 of file TensorIndices.h.
| void util::MoveFromPointers | ( | Coll & | dest, |
| PtrColl & | src | ||
| ) |
Moves the content from a collection of pointers to one of data.
| Coll | type of collection of data |
| PtrColl | type of collection of pointers to data |
| dest | collection to be filled |
| src | collection with the pointers to data to be moved |
The data pointed from each pointer in src is moved into dest. The destination collection is cleared first, and Coll must support both clear() and push_back()
Definition at line 57 of file SortByPointers.h.
References util::details::MoveFromPointersImpl< Coll, PtrColl >::move(), and SortByPointers().
Referenced by SortByPointers().
|
inline |
Based on operator==.
Definition at line 513 of file VectorMap.h.
| bool util::operator!= | ( | TensorIndices< RANK1 > const & | a, |
| TensorIndices< RANK2 > const & | b | ||
| ) |
Comparison operator with tensors of different rank.
Definition at line 524 of file TensorIndices.h.
Referenced by util::TensorIndices< DIMS >::operator!=().
|
inline |
Definition at line 501 of file VectorMap.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 105 of file ChangeTrackers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 206 of file ChangeTrackers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 319 of file ChangeTrackers.h.
|
inline |
Based on operator<.
Definition at line 529 of file VectorMap.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 494 of file VectorMap.h.
References util::VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare >::sortedVectorMap.
| bool util::operator== | ( | TensorIndices< RANK1 > const & | a, |
| TensorIndices< RANK2 > const & | b | ||
| ) |
Comparison operator with tensors of different rank.
Definition at line 516 of file TensorIndices.h.
Referenced by util::TensorIndices< DIMS >::operator==().
|
inline |
Based on operator<.
Definition at line 537 of file VectorMap.h.
| auto util::operator| | ( | Range && | range, |
| RangeForWrapperTag | |||
| ) | -> decltype(auto) |
Transforms a range so that it can be used in a range-for loop.
| Range | the type of range to be transformed |
| range | the range to be transformed |
This is necessary only when the argument provides different types for the begin-of-range and end-of-range iterators. This is also superfluous for compilers adhering to C++ 2017 standard, which accepts iterators of different types by requirement. Example of usage:
where data is supposed to gave begin and end iterators of different types.
Definition at line 460 of file RangeForWrapper.h.
References wrapRangeFor().
|
inline |
Returns the constant pi (up to 35 decimal digits of precision)
Definition at line 80 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by NuShowerEff::analyze(), util::GeometryUtilities::CalculatePitch(), apa::DisambigAlg::FindChanTimeEndPts(), art::FileDumperOutput::printPrincipal(), geo::OpDetGeo::ThetaZ(), and geo::WireGeo::WireGeo().
|
inline |
Converts the argument angle from radians into degrees ( 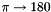 )
)
Definition at line 88 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by geo::OpDetGeo::ThetaZ(), and geo::WireGeo::ThetaZ().
| void util::SortByPointers | ( | Coll & | coll, |
| Sorter | sorter | ||
| ) |
Applies sorting indirectly, minimizing data copy.
| Coll | type of collection to be sorted |
| Sorter | type of sorter |
| coll | collection to be sorted |
| sorter | functor sorting a vector of pointers (makePointerVector()) |
The sorter functor can receive a reference to a vector as the one produced by makePointerVector(coll) (that is, a C++ STL vector of pointers to the value type of Coll), and sort it "in place". The container Comp must implement push_back() call in a std::vector fashion.
The algorithm is equivalent to the following:
sorter)Single elements are moved from the original collection to a new one.
The data elements of Coll must be moveable, as Coll itself must be.
Definition at line 127 of file SortByPointers.h.
References makePointerVector(), and MoveFromPointers().
Referenced by geo::CryostatGeo::CryostatGeo(), MoveFromPointers(), geo::GeometryCore::SortGeometry(), geo::CryostatGeo::SortSubVolumes(), and geo::PlaneGeo::SortWires().
|
inline |
See VectorMap::swap().
Definition at line 545 of file VectorMap.h.
References util::VectorMap< _Key, _Tp, _Compare >::swap().
| auto util::wrapRangeFor | ( | Range && | range | ) | -> decltype(auto) |
Wraps an object for use in a range-for loop.
| range | instance of the range object to be wrapped |
This is necessary only when the argument provides different types for the begin-of-range and end-of-range iterators. This is also superfluous for compilers adhering to C++ 2017 standard, which accepts iterators of different types by requirement. Example of usage:
where data is supposed to gave begin and end iterators of different types.
Definition at line 428 of file RangeForWrapper.h.
Referenced by operator|().
| constexpr double util::kBogusD = -999. |
obviously bogus double value
Definition at line 71 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by trkf::Geometric3DVertexFitter::addTrackToVertex(), recob::Vertex::chi2PerNdof(), recob::Event::Energy(), trkf::TrackKalmanFitter::fillResult(), trkf::Geometric3DVertexFitter::fitTwoTracks(), trkf::BezierTrack::GetSpacePointTrajectory(), wc::MergeWireCell::MakeShowers(), trkf::TrackState::mass(), trkf::TrajectoryMCSFitter::mass(), trkf::SpacePts::produce(), calo::Calorimetry::produce(), shwf::ShowerReco::produce(), trkf::CosmicTracker::produce(), evd::TWireProjPad::SaveSeedList(), recob::Event::SigmaEnergy(), evd::TWQProjectionView::UpdateSeedCurve(), recob::Vertex::Vertex(), and trkf::Geometric3DVertexFitter::weightedAverageState().
| constexpr float util::kBogusF = -999. |
obviously bogus float value
Definition at line 73 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by lar_pandora::LArPandoraTrackCreation::BuildTrack(), recob::Track::Chi2PerNdof(), trkf::Geometric3DVertexFitter::computeMeta(), and lar_pandora::LArPandoraTrackCreation::produce().
| constexpr int util::kBogusI = -999 |
obviously bogus integer value
Definition at line 72 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by lar_pandora::LArPandoraShowerCreation::BuildPCAxis(), lar_pandora::LArPandoraShowerCreation::BuildShower(), lar_pandora::LArPandoraTrackCreation::BuildTrack(), and recob::Vertex::Vertex().
| constexpr double util::kc = 29.9792458 |
Speed of light in vacuum in LArSoft units [cm/ns].
Definition at line 59 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by genf::GFEnergyLossBrems::energyLoss(), and genf::GFMaterialEffects::energyLossBrems().
| constexpr double util::kCentimeterToMeter = 1./kMeterToCentimeter |
Definition at line 64 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
| constexpr double util::keVToMeV = 1.e-6 |
1e6 eV = 1 MeV
Definition at line 68 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
| constexpr double util::kGeVToElectrons = 4.237e7 |
23.6eV per ion pair, 1e9 eV/GeV
Definition at line 55 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by util::LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT::BirksCorrection(), detinfo::DetectorPropertiesStandard::BirksCorrection(), lar_pandora::LArPandoraInput::GetMips(), sim::LArG4Parameters::GeVToElectrons(), util::LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT::ModBoxCorrection(), detinfo::DetectorPropertiesStandard::ModBoxCorrection(), and showerreco::ShowerRecoAlg::RecoOneShower().
| const double util::kINVALID_DOUBLE = std::numeric_limits<Double_t>::max() |
Definition at line 35 of file GeometryUtilities.h.
Referenced by util::GeometryUtilities::Get3DaxisN().
| constexpr double util::kKilometerToMeter = 1./kMeterToKilometer |
Definition at line 66 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
| constexpr double util::kMeterToCentimeter = 1.e2 |
1 m = 100 cm
Definition at line 63 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
| constexpr double util::kMeterToKilometer = 1.e-3 |
1000 m = 1 km
Definition at line 65 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
| constexpr double util::kMeVToeV = 1./keVToMeV |
Definition at line 69 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
| constexpr double util::kModBoxA = 0.930 |
Modified Box Alpha.
Definition at line 49 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by util::LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT::ModBoxCorrection(), detinfo::DetectorPropertiesStandard::ModBoxCorrection(), and sim::LArG4Parameters::reconfigure().
| constexpr double util::kModBoxB = 0.212 |
Modified Box Beta in g/(MeV cm²)*kV/cm.
Definition at line 50 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by util::LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT::ModBoxCorrection(), detinfo::DetectorPropertiesStandard::ModBoxCorrection(), and sim::LArG4Parameters::reconfigure().
| constexpr double util::kRecombA = 0.800 |
A constant.
Definition at line 35 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by util::LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT::BirksCorrection(), detinfo::DetectorPropertiesStandard::BirksCorrection(), and sim::LArG4Parameters::reconfigure().
| constexpr double util::kRecombk = 0.0486 |
k constant, in g/(MeV cm²)*kV/cm.
Definition at line 36 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
Referenced by util::LArPropertiesServiceArgoNeuT::BirksCorrection(), detinfo::DetectorPropertiesStandard::BirksCorrection(), and sim::LArG4Parameters::reconfigure().
Definition at line 75 of file PhysicalConstants.h.
| constexpr RangeForWrapperTag util::range_for |
Constant to be used with operator|(Range&&, details::RangeForWrapperTag).
Definition at line 440 of file RangeForWrapper.h.
Referenced by associated_groups(), and associated_groups_with_left().
| const float util::SQRT_TWO_PI = 2.506628 |
Definition at line 18 of file GaussianEliminationAlg.h.